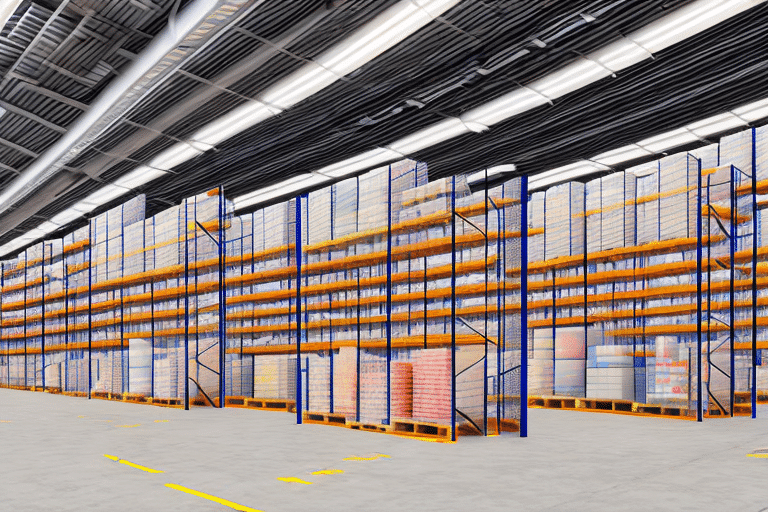
Conducting a Successful Warehouse Audit
As businesses grow and evolve, ensuring that warehouse operations run efficiently and effectively becomes paramount. Regular warehouse audits are essential for evaluating the entire inventory management system, from physical inventory checks to compliance with safety standards. This article explores the importance of warehouse audits, common issues identified, preparation steps, types of audits, and strategies for continuous improvement to enhance your warehouse operations.
The Importance of Regular Warehouse Auditing
Warehouse auditing is a critical process that helps businesses identify inefficiencies, potential safety hazards, and compliance issues. According to a Warehousing Education and Research Council (WERC) report, companies that conduct regular audits experience a 20% increase in inventory accuracy and a 15% improvement in operational efficiency. Regular audits ensure that warehouse operations remain streamlined, enhancing productivity and mitigating risks. Failure to perform these audits can lead to significant losses, lower customer satisfaction, and hindered business growth.
Moreover, regular auditing maintains high accuracy in inventory records, preventing issues like stockouts and overstocking. It also aids in detecting theft or loss, enabling timely corrective actions to safeguard assets.
Compliance with industry regulations is another crucial benefit. Regular audits help ensure adherence to standards, avoiding fines and legal complications. Additionally, they identify safety hazards, allowing businesses to implement measures that protect employees and maintain a safe working environment.
Common Problems Identified During Warehouse Audits
Warehouse audits frequently uncover a variety of issues that can hinder efficient operations. Common problems include:
- Inventory Inaccuracies: Discrepancies between physical inventory and records can lead to stockouts or overstocking.
- Operational Inefficiencies: Poor warehouse layout or unoptimized workflows can slow down processes and reduce productivity.
- Equipment Maintenance: Outdated or poorly maintained equipment increases the risk of malfunctions and accidents.
- Compliance Issues: Non-adherence to safety and regulatory standards can result in legal penalties and unsafe working conditions.
- Training Gaps: Lack of proper training for staff can lead to mishandling of inventory and safety practices.
Addressing these issues promptly ensures smoother warehouse operations and enhances overall efficiency.
Preparing for a Successful Warehouse Audit
Preparation is key to conducting an effective warehouse audit. Follow these essential steps to ensure a smooth audit process:
- Form an Audit Team: Include members from various departments to provide a comprehensive perspective.
- Develop a Checklist: Outline all areas and processes to be evaluated during the audit.
- Gather Documentation: Prepare necessary documents such as work orders, purchase orders, safety policies, and training records.
- Communicate with Staff: Inform all employees about the audit’s purpose and what to expect, fostering cooperation.
- Conduct a Preliminary Self-Audit: Identify and address potential issues before the official audit.
- Organize the Warehouse: Ensure inventory is properly labeled, aisles are clear, and equipment is in good working condition.
These preparatory steps maximize the audit’s effectiveness and minimize disruptions to daily operations.
Types of Warehouse Audits and Their Objectives
Understanding the different types of warehouse audits helps in selecting the appropriate approach for your business needs. Key types include:
Physical Inventory Audits
These audits focus on verifying the accuracy of inventory records by comparing them with the actual physical stock. Regular physical counts help identify discrepancies, reduce shrinkage, and ensure accurate inventory management.
Safety Audits
Safety audits evaluate compliance with occupational safety standards. They identify potential hazards, assess the effectiveness of safety protocols, and ensure that the warehouse environment is safe for employees.
Operational Audits
Operational audits assess the efficiency and effectiveness of warehouse processes. They examine workflows, storage systems, and resource utilization to identify areas for improvement and cost reduction.
Financial Audits
Financial audits review the accuracy of financial records related to warehouse operations. They ensure that financial transactions are correctly documented and comply with accounting standards.
Leveraging Technology and Key Metrics in Warehouse Audits
Integrating technology into warehouse audits enhances accuracy and efficiency. Tools such as warehouse management systems (WMS) and barcoding technologies automate inventory tracking and streamline audit processes. According to a Gartner study, warehouses using advanced technologies report a 30% reduction in audit time and a 25% increase in inventory accuracy.
Key metrics to measure during audits include:
- Inventory Accuracy: The degree to which inventory records match the physical stock.
- Order Fulfillment Speed: The time taken to process and ship orders.
- Shipping Accuracy: The rate of correct orders shipped without errors.
- Equipment Maintenance History: Records of equipment maintenance to prevent downtime.
Analyzing these metrics provides quantitative insights, enabling targeted improvements and informed decision-making.
Post-Audit Actions: Interpreting Results and Implementing Changes
Interpreting audit results effectively is crucial for driving improvements. Follow these steps:
- Review Findings: Assess each audit section to identify strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities.
- Develop an Action Plan: Create a strategy to address identified issues, involving input from relevant staff members.
- Set Goals: Establish measurable and achievable objectives to track the progress of implemented changes.
- Implement Changes: Execute the action plan, ensuring all team members are informed and involved.
- Monitor Progress: Continuously track the effectiveness of changes and make adjustments as necessary.
Addressing audit findings promptly enhances warehouse operations and supports continuous improvement.
Ensuring Compliance and Continuous Improvement
Maintaining compliance with industry regulations and fostering a culture of continuous improvement are essential for sustained warehouse performance. Best practices include:
- Regular Safety Training: Conduct ongoing training programs to ensure staff understand and adhere to safety protocols.
- Equipment Maintenance: Schedule regular maintenance to keep equipment in optimal condition and prevent accidents.
- Hazard Identification: Continuously assess the warehouse environment to identify and mitigate potential hazards.
- Continuous Auditing: Implement ongoing audit processes to identify trends, patterns, and areas for further improvement.
- External Audits: Engage external auditors periodically to gain an objective perspective and uncover blind spots.
By prioritizing compliance and continuous improvement, warehouses can enhance safety, efficiency, and overall operational excellence.
Training Your Staff on Proper Warehouse Audit Procedures
Effective warehouse audits depend on the competency of your staff. Training programs should cover:
- Audit Procedures: Educate staff on the steps and protocols involved in the audit process.
- Safety Standards: Ensure employees are aware of and adhere to safety guidelines to maintain a safe working environment.
- Inventory Management: Train staff on accurate inventory tracking and handling to reduce errors and discrepancies.
- Use of Technology: Provide training on warehouse management systems and other technologies used in audits.
Well-trained staff contribute to more accurate audits and efficient warehouse operations.
The Benefits of Conducting Regular Warehouse Audits for Business Growth
Regular warehouse audits offer numerous benefits that drive business growth:
- Enhanced Efficiency: Identifying and addressing inefficiencies streamlines operations and reduces costs.
- Improved Inventory Management: Accurate inventory records prevent stockouts and overstocking, ensuring optimal stock levels.
- Risk Mitigation: Early identification of safety hazards and compliance issues reduces the risk of accidents and legal penalties.
- Increased Customer Satisfaction: Efficient operations and accurate order fulfillment lead to higher customer satisfaction and repeat business.
- Competitive Advantage: Continuous improvement and optimal warehouse performance enable businesses to stay ahead in a competitive market.
By conducting regular audits, businesses can sustain growth, adapt to changing market demands, and maintain a high standard of warehouse operations.
Conclusion
Regular warehouse audits are indispensable for enhancing warehouse operations, ensuring compliance, and driving business growth. Through identifying inefficiencies, implementing necessary changes, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement, businesses can maintain optimal performance and adapt to evolving industry standards. Investing in comprehensive audit processes not only safeguards against risks but also positions businesses for sustained success in a competitive landscape.