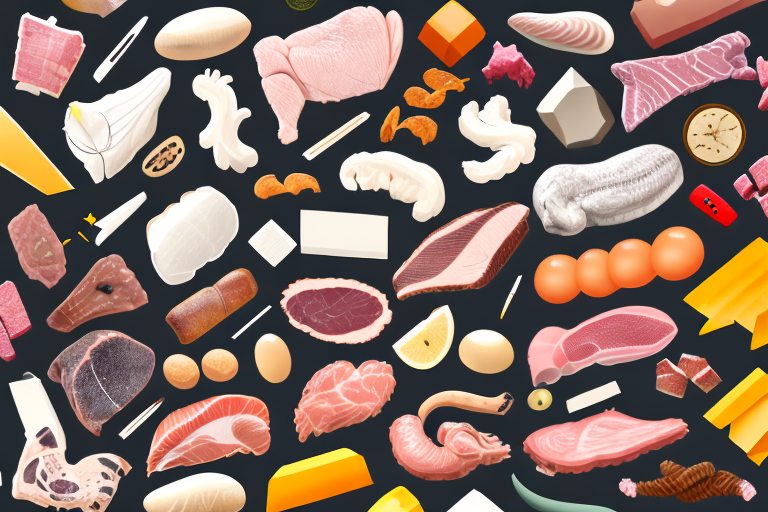
Understanding Blackbox Meats: A Sustainable Alternative
With the global demand for meat steadily increasing, the environmental and ethical implications of traditional meat production have become significant concerns. Blackbox meats, also known as lab-grown or cultured meats, offer a promising solution. This article delves into what blackbox meats are, their production process, and the myriad benefits they present in terms of nutrition, environmental sustainability, and consumer convenience.
The Production Process of Blackbox Meats
Cell Culturing and Growth
Blackbox meats are produced by cultivating animal cells in a controlled laboratory environment. The process begins with a small tissue sample from an animal, from which cells are extracted and placed in a nutrient-rich medium. These cells proliferate and differentiate into muscle tissue, forming the basis of the meat.
Technological Innovations
Advancements in bioreactor technology and cellular agriculture have significantly improved the efficiency and scalability of blackbox meat production. According to a study published in Nature, these innovations have reduced production costs by up to 60% in recent years.
Benefits of Blackbox Meat
Environmental Sustainability
Traditional livestock farming is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and water consumption. Blackbox meat production, on the other hand, requires significantly less land and water and emits fewer greenhouse gases. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change highlights lab-grown meats as a viable strategy to reduce the environmental footprint of food production.
Nutritional Advantages
Blackbox meats are nutritionally comparable to conventional meats, offering high protein content with the potential for customized nutritional profiles. Producers can modify the fat composition, increase essential nutrients, and eliminate harmful additives such as antibiotics and hormones.
Ethical Considerations
By eliminating the need to raise and slaughter animals, blackbox meats address significant animal welfare concerns. This method reduces the ethical dilemmas associated with traditional meat production, making it a more humane option.
Comparing Blackbox Meats to Traditional Meats
Taste and Texture
Advancements in food science have made blackbox meats nearly indistinguishable from their traditional counterparts in terms of taste and texture. Some studies suggest that cultured meats can achieve consistent quality, which is often variable in conventional farming due to factors like animal diet and living conditions.
Safety and Quality Control
The controlled production environment of blackbox meats minimizes the risk of contamination and foodborne illnesses. Unlike conventional meat, which can carry pathogens like E. coli and Salmonella, lab-grown meats are produced under sterile conditions, enhancing consumer safety.
Economic and Consumer Perspectives
Cost Considerations
While currently more expensive than traditionally farmed meats, the cost of blackbox meats is decreasing as technology advances and production scales up. Experts predict that prices could become competitive within the next decade, making sustainable meat options more accessible.
Consumer Acceptance
Initial consumer reviews of blackbox meats have been promising, with many praising their taste and ethical benefits. However, some skepticism remains regarding the safety and long-term health effects of consuming lab-grown meats. Ongoing education and transparent production practices are crucial for broader acceptance.
Addressing Common Myths and Misconceptions
There are several myths surrounding blackbox meats, such as the belief that they are not "real" meat or that their production involves genetic modification. In reality, blackbox meats are biologically identical to conventional meats and are produced using natural cellular processes without genetic alterations.
The Future of Blackbox Meat Technology
Looking ahead, blackbox meat technology holds significant potential for transforming the food industry. Continued research and investment are expected to drive down costs, improve production efficiency, and expand the range of available products. As the global population grows and environmental concerns intensify, blackbox meats could play a pivotal role in ensuring sustainable and ethical food sources.
Conclusion
Blackbox meat production represents a groundbreaking advancement in sustainable and ethical food production. With substantial benefits in environmental impact, nutrition, and animal welfare, it offers a viable alternative to traditional meat farming. As technology progresses and consumer awareness grows, blackbox meats are poised to become a mainstream option, contributing to a more sustainable and humane food system.