Understanding How Distribution Centers Work
In today's globalized world, efficient distribution centers are essential for businesses to meet customer demands and remain competitive in the market. Distribution centers act as a central hub for receiving, storing, and distributing goods to various locations. This article explores various aspects of distribution centers, including their types, importance, evolution over time, key components, warehouse management systems, best practices for managing them, challenges faced, and the future of distribution centers.
Types of Distribution Centers
Distribution centers come in different forms based on their function and the type of logistics they handle. Key types include:
- Retail Distribution Centers: Focused on distributing products to retail stores.
- Wholesale Distribution Centers: Sell goods in bulk to distributors or retailers.
- E-commerce Distribution Centers: Handle online sales and distribution of products.
- Mixed Distribution Centers: Manage a combination of the above activities.
- Cross-Docking Distribution Centers: Quickly transfer goods from incoming to outgoing trucks without long-term storage, commonly used in industries like food and beverage.
- Specialized Distribution Centers: Cater to specific industries or products, such as pharmaceutical or temperature-controlled distribution centers.
Understanding the type of distribution center needed for your business is vital in ensuring the efficient distribution of products.
The Role of Distribution Centers in the Supply Chain
Distribution centers are a vital component in the supply chain, ensuring that the right products reach the right places at the right time. They act as intermediaries between manufacturers and retailers, allowing for better inventory management and reducing transportation costs. According to a Statista report, efficient distribution centers can reduce operational costs by up to 30%.
Additionally, distribution centers provide value-added services such as packaging, labeling, and quality control to ensure products meet required standards before shipment. They also offer customization services like kitting, assembly, and product configuration to meet specific customer needs.
Moreover, distribution centers play a crucial role in managing returns and reverse logistics. By efficiently handling returned products, they help reduce waste and minimize environmental impact, contributing to better sustainability practices.
The Evolution of Distribution Centers Over Time
Over the years, distribution centers have evolved from manually operated facilities to highly automated hubs leveraging advanced technology. Initially, distribution centers relied on manual labor and paper-based systems for receiving, storing, and distributing goods. However, advancements in technology have introduced automation and computerization, significantly increasing efficiency and speed. Modern distribution centers utilize automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS), robotics, and sophisticated warehouse management systems (WMS) to handle higher volumes of products, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.
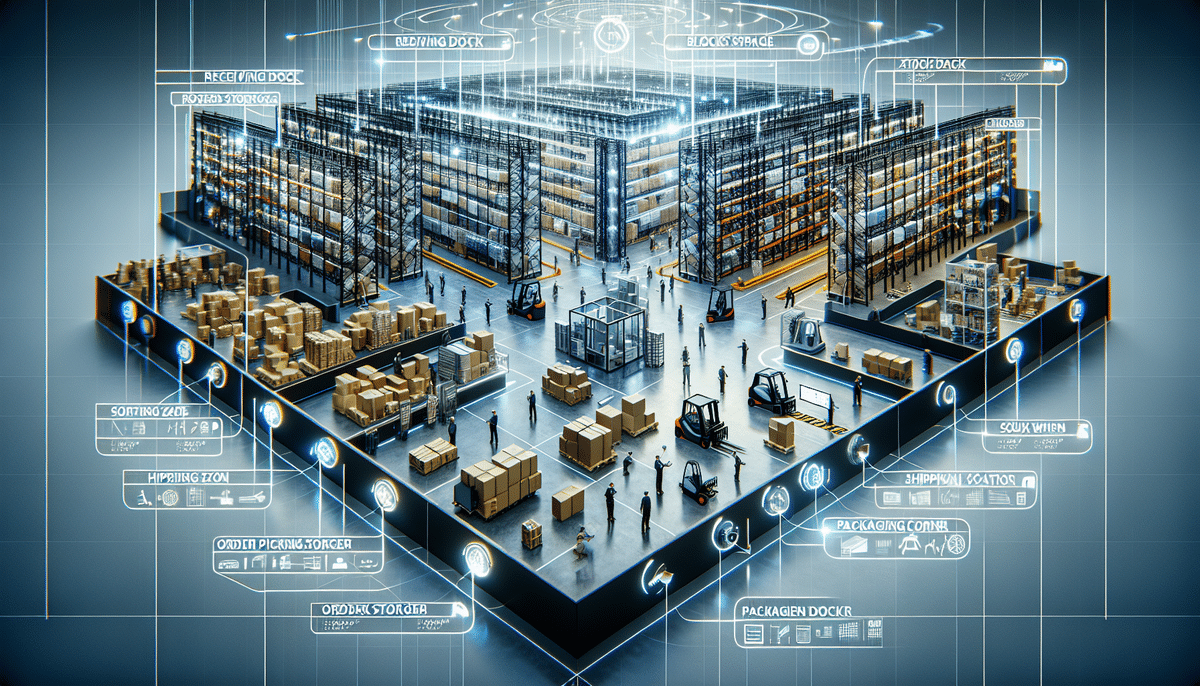
Key Components of a Distribution Center
A well-functioning distribution center comprises several key components:
- Receiving Dock: Where goods are received from manufacturers and checked for quality standards.
- Storage Area: Includes rack or block storage depending on the nature of the goods.
- Sorting Area: Responsible for categorizing products for shipment.
- Order Picking Area: Where products are selected based on customer orders.
- Packing Area: Products are packed and prepared for shipment.
- Shipping Dock: Where packed goods are dispatched to various destinations.
Warehouse Management Systems and Their Importance
Warehouse management systems (WMS) are critical for streamlining and automating distribution center operations. These systems enhance inventory control, expedite order processing, and improve fulfillment accuracy. By automating manual processes, businesses can increase productivity, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction. Modern WMS solutions offer features such as real-time inventory tracking, order picking optimization, and comprehensive reporting capabilities.
Implementing a robust WMS can lead to significant improvements in operational efficiency. According to a report by Warehouse Management, businesses can achieve a 25% increase in operational efficiency by adopting advanced WMS technologies.
Best Practices for Managing a Distribution Center
Effective management of a distribution center involves several best practices:
- Maintain Accurate Inventory: Implement reliable inventory tracking systems to prevent discrepancies.
- Optimize Layout: Design the distribution center layout for maximum efficiency and minimal movement.
- Continuous Employee Training: Regularly train staff to handle new technologies and procedures.
- Listen to Customer Feedback: Use feedback to improve processes and service quality.
- Ensure Proper Inventory Rotation: Implement strategies like FIFO (First-In, First-Out) to manage stock effectively.
- Follow Safety Protocols: Maintain a safe working environment to prevent accidents and injuries.
- Maintain Flexibility: Adapt schedules and operations to handle peak periods efficiently.
Consistently applying these practices can significantly enhance the efficiency and productivity of your distribution center.
Challenges Facing Distribution Centers Today
Distribution centers face several challenges that can impact their effectiveness:
- Rising Operational Costs: Increased expenses related to labor, utilities, and maintenance.
- Labor Shortages: Difficulty in finding and retaining skilled workers.
- Inventory Forecasting: Accurately predicting demand to manage stock levels.
- Demand for Fast Delivery: Pressure to offer quicker delivery times to meet customer expectations.
- Sustainability Practices: Implementing eco-friendly operations to reduce environmental impact.
Addressing these challenges is essential for maintaining high performance and competitiveness in the market.
The Future of Distribution Centers
The future of distribution centers is set to be shaped by continuous technological advancements. Key trends include:
- Automation and Digitalization: Increased use of robotics, autonomous vehicles, and automated storage systems.
- Enhanced Data Analysis: Leveraging big data and artificial intelligence for better inventory forecasting and demand planning.
- Drones and Robotics: Utilizing drones for inventory management and robotics for order fulfillment.
- 24/7 Operations: Implementing technologies that enable round-the-clock operations and delivery services.
Logistics companies investing in these technologies will likely maintain a competitive edge by offering faster, more efficient distribution services.
Comparison Between Traditional vs. Automated Distribution Centers
Traditional distribution centers rely heavily on manual labor and paper-based systems, while automated distribution centers utilize advanced technologies to streamline operations. Here are some key differences:
- Efficiency: Automated centers handle larger volumes of products more quickly and accurately.
- Cost: Automation can reduce long-term operational costs despite high initial investments.
- Accuracy: Automated systems minimize human errors in order fulfillment.
- Flexibility: Traditional centers may better handle customized orders and complex supply chains.
Businesses must evaluate the pros and cons of each type to determine which best suits their operational needs and strategic goals.
Case Studies: Successful Distribution Center Operations
Several companies have demonstrated excellence in distributing center operations:
- Amazon: Known for its highly efficient and technologically advanced distribution centers, Amazon leverages robotics and sophisticated WMS to manage vast inventories and expedite order fulfillment.
- Walmart: Utilizes a robust distribution network and advanced logistics to ensure products are available in stores and for online orders.
- Target: Employs strategic distribution center locations and technology to optimize supply chain operations.
- Nike: Implements sustainable practices and efficient distribution strategies to meet global demand.
These companies have invested in technologies, optimized their layouts, and trained their staff to achieve high levels of service and efficiency.
Tips for Optimizing Your Distribution Center's Efficiency and Productivity
To optimize efficiency and productivity in your distribution center, consider the following tips:
- Implement Warehouse Management Systems: Utilize WMS to automate processes and improve accuracy.
- Monitor Inventory Levels: Keep track of stock to prevent overstocking or understocking.
- Optimize Layout: Design the distribution center layout to minimize movement and maximize space utilization.
- Adopt Lean Management Strategies: Eliminate waste and streamline operations for better efficiency.
- Set Up Forecasting Systems: Improve planning and inventory management through accurate demand forecasting.
- Use Real-Time Tracking and Monitoring: Enhance visibility into operations for better decision-making and problem-solving.
The Relationship Between E-commerce and Distribution Centers
The surge in e-commerce has significantly influenced the role and importance of distribution centers. E-commerce distribution centers are specifically designed to handle online orders and shipping efficiently. Benefits include:
- Quick and Efficient Shipping: Reduces transportation costs and delivery times.
- Strategic Location: Placed near densely populated areas to facilitate faster delivery.
- Scalability: Easily scalable to handle fluctuating order volumes.
This strategic alignment helps businesses meet the increasing demands of online consumers while maintaining cost-effectiveness.
Environmental Impact of Distribution Centers and Sustainable Practices
The expansion of distribution centers, particularly due to the growth of e-commerce, has raised concerns about environmental impact, including increased packaging waste and greenhouse gas emissions from transportation. Sustainable practices can mitigate these impacts:
- Alternative Fuels: Using eco-friendly fuels for transportation to reduce emissions.
- Sustainable Packaging: Designing packaging that minimizes waste and is recyclable.
- Optimizing Transportation Routes: Reducing fuel consumption and emissions by planning efficient delivery routes.
- Energy-Efficient Systems: Implementing energy-efficient lighting, heating, and cooling systems in distribution centers.
- Recycling Programs: Encouraging recycling to reduce overall waste.
Adopting these sustainable practices not only benefits the environment but can also lead to cost savings and improved corporate reputation.
How Technology is Changing the Landscape of Distribution Centers
Technology continues to transform distribution centers, enhancing efficiency and productivity. Key technological advancements include:
- Real-Time Tracking and Monitoring: Provides visibility into inventory movements and operational processes.
- Warehouse Management Systems: Automate inventory control, order processing, and fulfillment.
- Robotic Automation: Utilizes robots for tasks like picking, packing, and sorting to increase speed and accuracy.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Leverages big data and analytics for inventory control and demand forecasting.
These technologies enable businesses to handle more products, reduce transportation costs, and enhance customer satisfaction by ensuring timely and accurate deliveries.
Comparison Between Centralized vs. Decentralized Distribution Centers
The choice between centralized and decentralized distribution centers depends on a business's distribution strategy:
- Centralized Distribution Centers: More efficient for handling large volumes of products and cost-effective due to shared space and equipment.
- Decentralized Distribution Centers: Allow for faster delivery times by storing products closer to customers but can be more expensive to operate due to the need for separate staff and equipment for each center.
Businesses must assess their specific needs, customer locations, and budget constraints to determine the most suitable distribution strategy.
The Importance of Location in Setting Up Distribution Centers
The location of a distribution center significantly impacts transportation costs, delivery times, and overall customer satisfaction. Key factors to consider when selecting a location include:
- Proximity to Customers: Closer locations can reduce delivery times and transportation costs.
- Availability of Labor: Access to a skilled workforce is essential for efficient operations.
- Cost of Real Estate: Balancing location benefits with real estate costs is crucial for budget management.
- Transportation Infrastructure: Easy access to major highways, ports, and airports facilitates efficient distribution.
A well-located distribution center can enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Cost-Benefit Analysis for Setting Up a New Distribution Center
Before establishing a new distribution center, conducting a comprehensive cost-benefit analysis is essential to determine its feasibility. This analysis should consider:
- Real Estate Costs: Expenses related to purchasing or leasing property.
- Equipment Costs: Investment in machinery, technology, and other necessary equipment.
- Labor Costs: Salaries, training, and benefits for employees.
- Transportation Costs: Expenses related to shipping and logistics.
- Potential Returns on Investment: Projected revenue increases and cost savings from improved operations.
- Expected Efficiency Gains: Improvements in productivity and customer satisfaction.
By thoroughly analyzing these factors, businesses can make informed decisions about the establishment of new distribution centers and ensure strategic alignment with their overall goals.
Real-Time Tracking and Monitoring Systems for Efficient Distribution Center Management
Real-time tracking and monitoring systems are pivotal for effective distribution center management. These systems offer several benefits:
- Inventory Movement Tracking: Provides visibility into the location and status of products within the distribution center.
- Inventory Level Monitoring: Ensures optimal stock levels to meet demand without overstocking.
- Data Analytics: Facilitates informed decision-making through comprehensive data insights.
- Issue Alerts: Notifies management of any operational issues in real time, enabling prompt resolutions.
Implementing real-time tracking systems enhances operational transparency, reduces errors, and improves overall efficiency in distribution center management.
Understanding the Role of Inventory Management in Distribution Centers
Inventory management is critical in managing distribution centers and significantly impacts a business's profitability. Effective inventory management involves:
- Understanding Inventory Levels: Maintaining accurate records of stock to prevent discrepancies.
- Demand Forecasting: Predicting customer demand to manage stock levels appropriately.
- Inventory Rotation: Ensuring that older stock is sold before newer stock to prevent obsolescence.
Adopting a sound inventory management system reduces inventory carrying costs, eliminates overstocking or understocking, and improves order fulfillment accuracy.
In conclusion, understanding how distribution centers work enables businesses to streamline operations, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction. By recognizing the types of distribution centers, their role in the supply chain, evolution over time, and key components, businesses can optimize their operations. Implementing warehouse management systems, monitoring inventory levels, and optimizing layouts are best practices that increase efficiency and productivity. Addressing the challenges faced by distribution centers, understanding future trends, and adopting sustainable practices are also vital for long-term success.