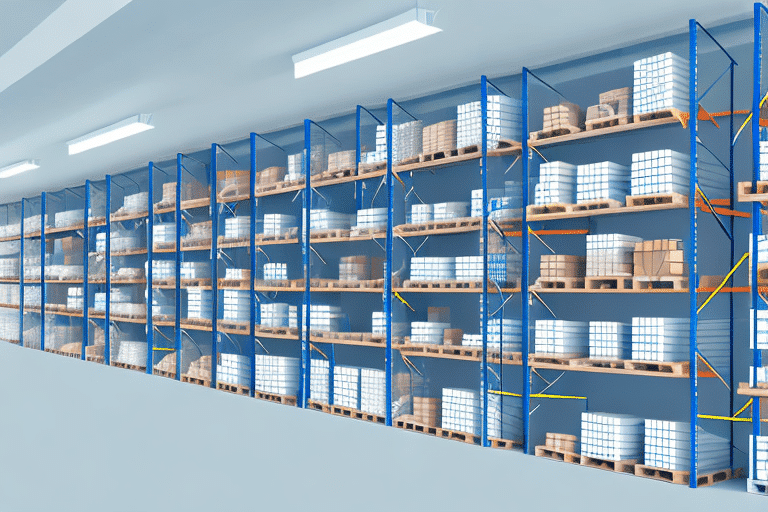
Understanding the Benefits of a Periodic Inventory System
If your business handles physical inventory, implementing an efficient inventory system is crucial. A periodic inventory system is one approach that can help you monitor and manage inventory levels effectively. This article dives deep into periodic inventory systems, exploring their benefits, implementation strategies, and how they compare to other inventory management methods.
What is a Periodic Inventory System?
A periodic inventory system is a method of inventory management that relies on manual physical counts of inventory to determine stock levels. Unlike perpetual inventory systems, which keep continuous track of inventory, periodic systems involve counting inventory at fixed intervals—such as weekly, monthly, quarterly, or annually. The results of these counts are used to update inventory records, reflecting the quantity and value of stock on hand.
Businesses using a periodic system maintain detailed records of inventory purchases, sales, and returns throughout the period. At the end of the period, these records are reconciled with the physical count to calculate the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) and inventory valuation.
Advantages of a Periodic Inventory System
Cost-Effective Implementation
One of the primary advantages of a periodic inventory system is its simplicity and low cost. It does not require specialized software or equipment, making it accessible for small businesses or those with limited resources.
Flexibility
Periodic systems can be customized to fit the unique needs of a business. Whether you prefer weekly counts or annual audits, the system can adapt to your operational requirements.
Simplicity
The straightforward nature of periodic inventory systems makes them easy to understand and manage. This simplicity reduces the likelihood of errors that can occur with more complex systems.
Accurate Inventory Records
Regular physical counts ensure that inventory records are periodically updated, helping to maintain accuracy and minimize discrepancies.
Comparing Periodic and Perpetual Inventory Systems
While both systems aim to manage inventory effectively, they operate differently:
- Periodic Inventory System: Updates inventory levels at specific intervals through physical counts.
- Perpetual Inventory System: Continuously tracks inventory in real-time using digital tools.
Perpetual systems offer more precise and timely inventory data but can be more costly and complex to implement. Periodic systems, on the other hand, are simpler and more affordable but may lack real-time accuracy.
Implementing a Periodic Inventory System
Best Practices
- Regular Count Schedule: Establish and adhere to a consistent inventory count schedule.
- Staff Training: Ensure that employees are trained in accurate inventory counting and record-keeping procedures.
- Error Checking: Regularly compare physical counts with inventory records to identify and correct discrepancies.
- Consistent Storage: Store inventory items in a standardized and accessible manner to facilitate accurate counting.
- Proper Labeling: Use labels and barcodes to simplify inventory identification and tracking.
Choosing the Right Software
If you opt to integrate digital tools with your periodic system, consider the following when selecting inventory management software:
- Cost-effectiveness
- User-friendliness
- Customization options
- Integration capabilities with your accounting system
- Scalability to grow with your business
Calculating Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) with a Periodic System
Calculating COGS in a periodic inventory system involves the following steps:
- Determine Beginning Inventory: Start with the inventory value at the beginning of the period.
- Add Purchases: Include all inventory purchases made during the period.
- Subtract Returns and Allowances: Deduct any returns or allowances from the total purchases.
- Calculate Cost of Goods Available for Sale: Sum the beginning inventory and net purchases.
- Conduct Physical Count: Perform a physical inventory count to determine ending inventory levels.
- Determine COGS: Subtract the ending inventory from the cost of goods available for sale.
While this process can be time-consuming, it ensures that COGS accurately reflects the inventory sold during the period.
Overcoming Common Challenges
Periodic inventory systems can present several challenges, including:
- Inaccurate inventory counts
- Slow reporting processes
- Difficulty detecting shrinkage or theft promptly
- Tracking inventory levels for fast-moving items
To address these challenges, consider adopting a hybrid approach that combines periodic counts with elements of a perpetual system. This can provide more accurate inventory tracking while maintaining the cost-effectiveness of a periodic system.
The Financial Impact of Effective Inventory Management
Poor inventory management can negatively affect your business's financial health. Issues like stockouts can lead to lost sales and diminished customer satisfaction, while overstocks can result in unnecessary carrying costs and reduced profitability. Additionally, inaccurate inventory records can cause discrepancies in financial reporting, leading to potential tax and compliance issues.
Implementing an effective periodic inventory system helps mitigate these risks by ensuring accurate inventory levels and reliable financial data, ultimately supporting better financial decision-making and improved profitability.
Conclusion
A periodic inventory system offers numerous benefits, including cost savings, simplicity, and flexibility. By regularly monitoring inventory levels and adhering to best practices, businesses can reduce the risk of stockouts, overstocks, and shrinkage. Implementing an effective periodic inventory system requires discipline and attention to detail, but the rewards in terms of increased profitability and operational efficiency are well worth the effort.